IQM Achieves Quantum Computing Profitability by Emulating SpaceX's Early Revenue Model
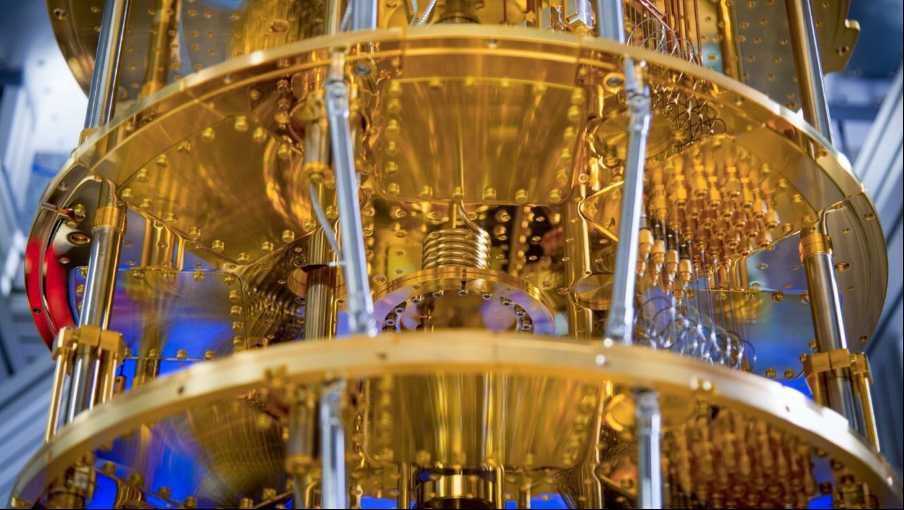
Finnish quantum computing firm IQM has achieved early-stage profitability by leveraging a SpaceX-inspired strategy of selling pre-commercial quantum systems to government-backed research institutions and supercomputing centers, CEO Jan Goetz announced at The Next Web (TNW) conference. This approach has generated over €90 million ($100 million) in orders since its 2018 founding, with 13 quantum computers sold globally. The company’s diversified revenue streams—combining hardware sales, cloud-based compute time, and maintenance services—mark a critical milestone in quantum technology’s commercialization.
Source: Images from the Internet, if there is any infringement, please contact the removal of
-
Pre-Commercial Hardware Sales
IQM’s core strategy involves delivering development-stage quantum computers to organizations like the EuroHPC Joint Undertaking, which recently ordered two systems (54 and 150 qubits) for €25 million 2. These partnerships provide crucial R&D funding while establishing early adopters. For instance, the Finnish VTT Technical Research Centre purchased a 300-qubit system in 2025, including a cloud platform and maintenance contract . By 2025, IQM’s manufacturing facility will produce 20 quantum computers annually, supported by Europe’s only private quantum chip fabrication line .
-
Cloud Ecosystem Expansion
The IQM Resonance cloud platform, upgraded in July 2025, now offers access to a 54-qubit system (driven by the Crystal 54 chip) and supports advanced tools like the Qrisp SDK for algorithm development 4. Over 200 institutions globally use the platform, with free tier access attracting students and researchers. This model mirrors SpaceX’s early reliance on NASA contracts to fund rocket development, creating recurring revenue through cloud subscriptions and enterprise partnerships.
-
Multi-Sector Diversification
Beyond academic and government clients, IQM targets industries like pharmaceuticals and finance. For example, its quantum systems are used to simulate complex molecular interactions for drug discovery—a capability highlighted in recent studies combining quantum computing with AI 8. The company’s full-stack product portfolio, ranging from €1M entry-level Spark systems to 150-qubit Radiance machines, caters to diverse market segments .
While IQM’s success signals progress, CEO Goetz warned that Europe risks falling behind in quantum competition due to insufficient private investment. The region attracts just 5% of global quantum funding, compared to 50% in the U.S. and 40% in China 5. This contrasts with IQM’s €128M Series A2 funding in 2022—the largest European quantum investment to date 1. To sustain momentum, Goetz emphasized the need for public-private partnerships and infrastructure quantumization, such as integrating quantum capabilities into data centers .
IQM identifies two primary growth vectors:
- Infrastructure Quantumization: Integrating quantum accelerators into supercomputing hubs, similar to China’s "Tianyan" quantum cloud platform, which connects 504-qubit systems to national supercomputing networks .
- AI Training Optimization: Using quantum computers to generate high-quality training data for machine learning, a frontier explored by companies like Insilico Medicine in drug discovery .
IQM’s profitability contrasts with competitors like IBM and Google, which focus on long-term R&D. While IBM’s 1,121-qubit Condor chip dominates technical benchmarks , IQM’s hardware-first approach addresses immediate market needs. Analysts note that IQM’s model could accelerate quantum adoption, but scaling profitability will require overcoming error correction challenges—a hurdle Google aims to tackle with its 105-qubit Willow chip by 2029 .
As the quantum race intensifies, IQM’s hybrid strategy of hardware sales, cloud services, and strategic partnerships positions it as a trailblazer in translating academic breakthroughs into tangible commercial value. The company’s success underscores the importance of multi-stakeholder collaboration in bridging the gap between quantum research and real-world applications.
This article synthesizes IQM’s commercialization milestones with industry trends, highlighting its unique position in balancing technical innovation with sustainable revenue models. The analysis integrates insights from EuroHPC collaborations , cloud platform upgrades , and European funding dynamics 5 to provide a comprehensive view of quantum computing’s evolving landscape.